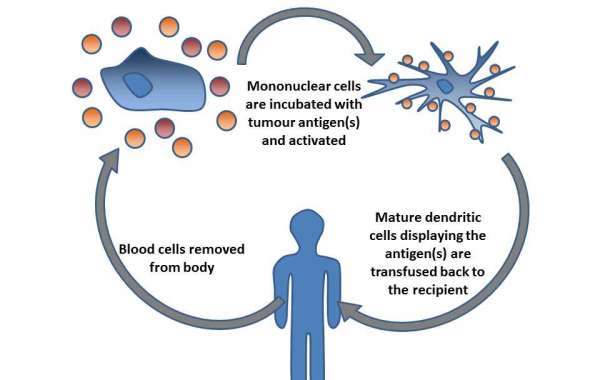
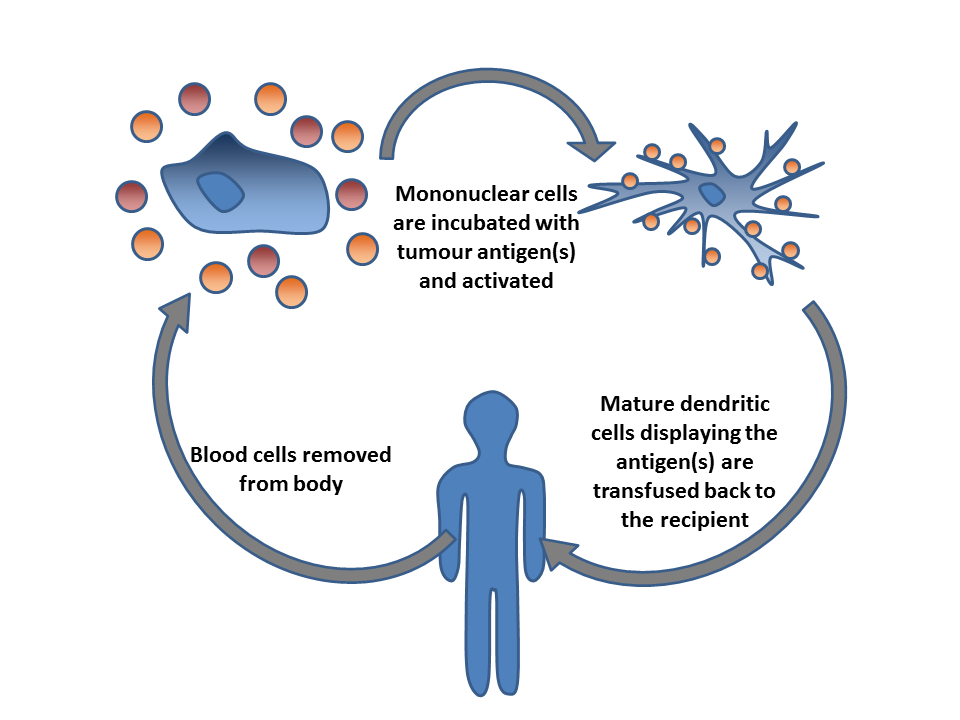
Dendritic cells (DCs), traditionally known for their pivotal role in cancer immunotherapy, are now at the forefront of innovative approaches for non-cancer indications. This article explores the burgeoning potential of DC therapy in treating autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and chronic inflammatory conditions. Examining trending examples such as DCs loaded with tolerogenic antigens for rheumatoid arthritis and DC-based vaccines for chronic hepatitis B, we delve into the transformative landscape of non-cancer applications for Dendritic Cell therapy.
Unlocking the Potential: DC Therapy Beyond Cancer
Dendritic cell therapy, once exclusively associated with cancer treatment, is expanding its horizons to address a spectrum of non-cancer indications. This shift reflects the versatility of DCs and their unique ability to modulate immune responses. We explore how DCs are emerging as key players in revolutionizing treatment strategies for autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and chronic inflammatory conditions.
Tolerogenic DCs: A Precision Approach to Rheumatoid Arthritis
In the quest for effective treatments for autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), tolerogenic dendritic cells have emerged as a promising avenue. A study published in Frontiers in Immunology (link here) investigates the potential of DCs loaded with tolerogenic antigens to regulate immune responses in RA. This precision approach showcases how DC therapy can be tailored to modulate the immune system, offering hope for more targeted and efficient interventions in autoimmune conditions.
DCs as Antigen Platforms: Crafting Vaccines Against Chronic Viral Infections
DCs, serving as potent antigen-presenting cells, are now harnessed as platforms for developing vaccines against chronic viral infections. A compelling example is explored in a study published in Frontiers in Immunology (link here), focusing on dendritic cell-based vaccines for chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. By leveraging the unique capabilities of DCs, researchers are pioneering a new frontier in vaccine development, aiming to combat persistent viral infections more effectively.
Navigating the Landscape: Challenges and Opportunities
While the potential of DC therapy for non-cancer indications is promising, challenges and opportunities shape its trajectory. From optimizing DC maturation protocols to ensuring sustained immune modulation, researchers are actively addressing hurdles. The adaptability of DCs and their ability to orchestrate immune responses, however, offer a platform for innovative solutions, presenting a landscape ripe with possibilities for advancing non-cancer treatment modalities.
Conclusion: DC Therapy Redefined in the Non-Cancer Arena
Dendritic cell therapy, once synonymous with cancer immunotherapy, is now rewriting the narrative in non-cancer treatment realms. From the precision targeting of autoimmune responses in rheumatoid arthritis to crafting vaccines against chronic viral infections, DCs are at the forefront of innovation. As we navigate this transformative landscape, the versatility of DC therapy unveils new avenues for addressing the complexities of non-cancer indications, marking a paradigm shift in immunotherapy strategies.
References: