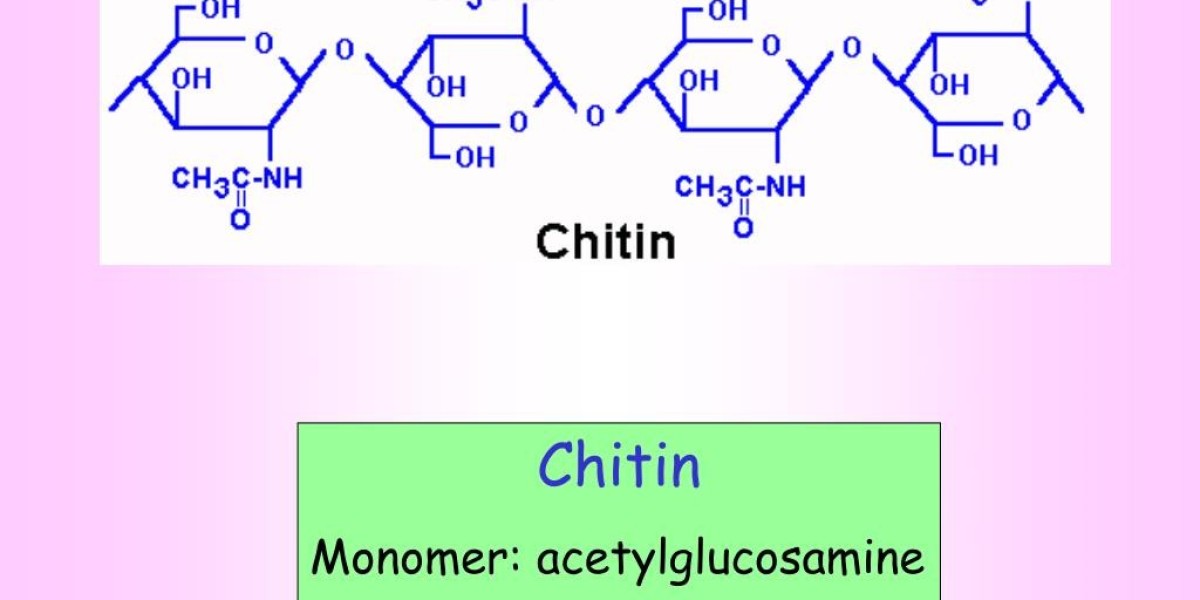
Formation and Structure of Chitin
Chitin is a long-chain polymer of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and is found in the exoskeleton of crustaceans like crabs, lobsters, and shrimp as well as cell walls of fungi and yeast. It is formed in vivo by residing enzymes through a metabolic pathway known as N-acetylglucosamine synthesis. N-acetylglucosamine has a linear chain molecular structure consisting of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine units linked together by beta-1,4-glycosidic bonds. These chains further associate laterally through hydrogen bonding to form microfibrils which self-assemble into insoluble extended structures. The arrangement and packing of molecular chains give N-acetylglucosamine its tensile strength, flexibility and resilience.
Abundance and sources of Chitin
Chitin is one of the most abundant biopolymers on earth, second only to cellulose. It is estimated that 10^11-10^12 tons of N-acetylglucosamine is produced globally per year. Seafood waste from fishing industry and shellfish farming is a major source of N-acetylglucosamine. Crabs alone produce over 1 million tons of N-acetylglucosamine annually. Fungal cell walls during fermentation processes also generate huge amounts of N-acetylglucosamine. Besides natural sources, N-acetylglucosamine can also be produced through chemical or enzymatic biosynthesis. By unlocking underutilized streams, N-acetylglucosamine availability can be substantially scaled up to meet industrial needs.
Physico-Chemical Properties of Chitin
Chitin exhibits unique physico-chemical properties which make it suitable for wide range of applications. It has high tensile strength, flexibility and permeability to liquids and gases. Being a semi-crystalline polymer, N-acetylglucosamine shows polymorphism depending on hydration and processing conditions. Its crystalline regions impart strength while amorphous domains provide elasticity. N-acetylglucosamine is remarkably stable in polar solvents and resistant to heat, acids and bases. However, it is not soluble in common solvents and requires alkaline or enzymatic treatments for functionalization. N-acetylglucosamine has immense capacity to absorb organic liquids and metal ions from solutions through chelation. These properties lend it remarkable processing versatility.
Applications of N-acetylglucosamine in Different Sectors
Biomedical applications: Due to its biocompatibility and non-toxic nature, N-acetylglucosamine finds various uses in biomedical field as wound dressings, surgical sutures, bone graft substitutes, drug delivery carriers and scaffolds for tissue engineering. Research is on to exploit its novel properties like reactive amino groups and hydrating ability in biomedicine.
Pharmaceutical applications: Use of N-acetylglucosamine as excipient, disintegrant and biosorbent holds immense potential in pharmaceutical sector especially for controlled drug delivery. Its mucoadhesive property helps in producing medicated formulations for ocular, oral and topical uses. Recent studies have explored its role in antiviral, anti-tumor and immunostimulatory drug development.
Food applications: N-acetylglucosamine forms core part of promising applications like clarifying agent in beverages, fat substitute, thickener, stabilizer and emulsifier for low calorie foods. It acts as prebiotic fiber and provides textural benefits. Industries are utilizing it in enhanced functional foods as well as nutraceuticals and dietary supplements. Chitosan's bioactivity is being studied to develop novel anticaking and anticorrosion agents for food processing.
Water treatment applications: Ability of N-acetylglucosamine to bind heavy metals and removal of pathogenic microbes has magnified its significance in water treatment processes. It is employed in preparation of membranes and filters, chelation polymers and coagulants to remedy industrial effluents and contaminated water bodies. Research uncovers potential applications in desalination and resource recovery from wastewater.
Agricultural and environmental applications: Development of superabsorbent polymers from N-acetylglucosamine and its derivatives has expanded agricultural uses as water retaining agents or carriers of agrochemicals. Their film forming property and antifungal action supports biocontrol strategies. N-acetylglucosamine waste utilization in fertilizers manufacture cuts pollution load and boosts sustainable agriculture complementing circular economy models.
Other applications: Besides above, N-acetylglucosamine materials play critical role in diverse industrial sectors through their chemical and physical attributes. These include development of paperboards, photographic films, adhesives, paints, cosmetics, textiles, biosensors along with their employment as fining agents in food and metal extraction industries. Rise of bionanocomposites paves way for futuristic photonic, optoelectronic and energy applications using N-acetylglucosamine.
N-acetylglucosamine has emerged as a renewable, eco-friendly and versatile biomass material with broad scope for commercialization. Its sourcing from abundant waste streams offers sustainable solution to develop value-added products replacing synthetic polymers. Multidisciplinary research is expanding diverse application domains while improving production methods. With advancements in processing techniques and chemical modifications, N-acetylglucosamine based biomaterials are poised to make significant global economic and environmental impact in years to come. Optimization of industrial scale production holds key to realize its commercial potential. Overall, N-acetylglucosamine acts as a promising platform to build sustainable circular bioeconomy.
Get More Insights on- Chitin
For Deeper Insights, Find the Report in the Language that You want:
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)