BMI calculators are tools designed to help people determine their BMI quickly and easily. This article explores what BMI is, how to use a BMI calculator, its significance, limitations, and why it remains a valuable tool in health and wellness assessments.
What is BMI?
BMI is a simple measurement that compares an individual’s weight and height to categorize their body weight as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese. It does not measure body fat directly, but it offers a general indicator of whether a person’s weight might put them at risk for health problems associated with being underweight or overweight. BMI was developed by the Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet in the 19th century and remains widely used today.
The BMI formula is straightforward:
BMI=weight (kg)height2 (m2)BMI = \frac{weight \, (kg)}{height^2 \, (m^2)}BMI=height2(m2)weight(kg)To break this down:
- Weight is measured in kilograms (kg).
- Height is measured in meters (m).
For example, if you weigh 70 kilograms and your height is 1.75 meters, the BMI is calculated as:
BMI=701.752=703.0625=22.86BMI = \frac{70}{1.75^2} = \frac{70}{3.0625} = 22.86BMI=1.75270=3.062570=22.86This number, 22.86, falls within the "Normal weight" range, according to the BMI categories discussed below.
What is a BMI Calculator?
A BMI calculator is a tool that automates the process of calculating your BMI. It eliminates the need to manually apply the formula and interpret the result. These calculators are available on various platforms, such as websites, apps, and even in some fitness trackers. You simply input your weight and height, and the calculator provides you with a BMI number, along with a categorization based on that value.
BMI calculators have become a convenient and efficient way for individuals and healthcare professionals to monitor health risks associated with weight. Many online tools also provide suggestions or recommendations on how to manage weight, based on the results.
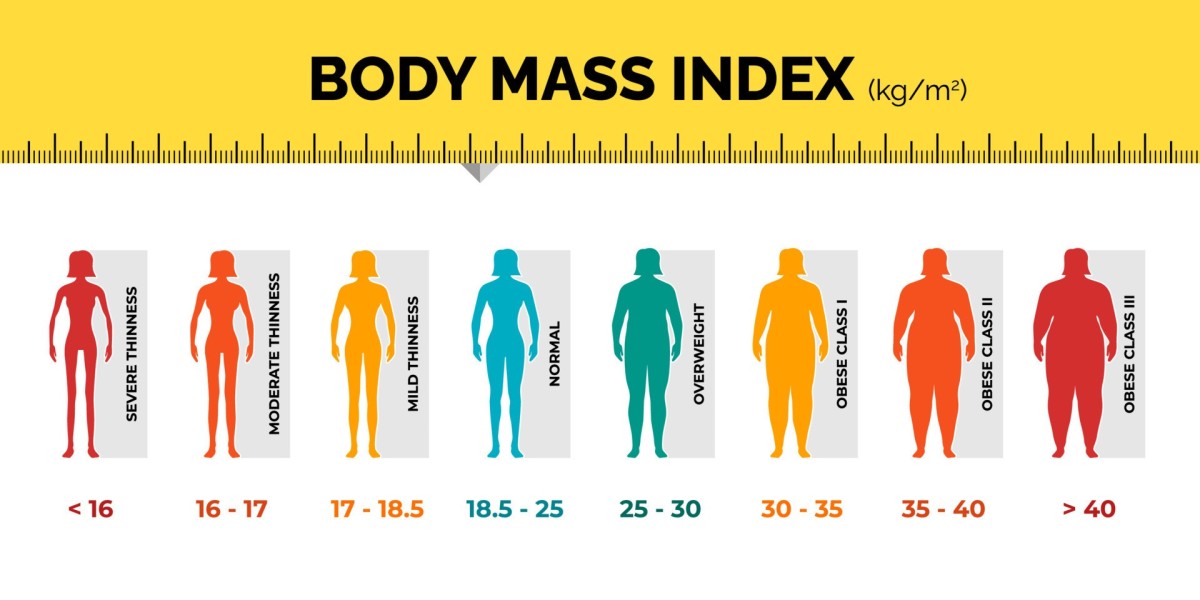
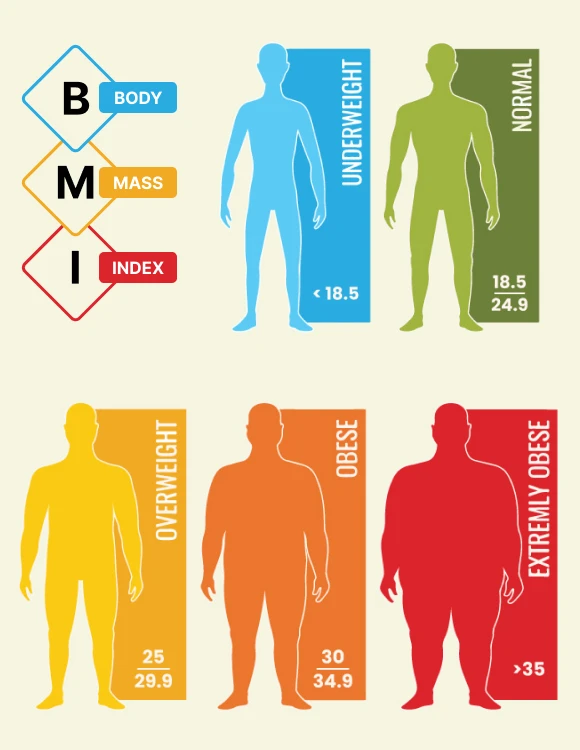
BMI Categories: What Do They Mean?
Once your BMI is calculated, it falls into one of the following categories, which are established by the World Health Organization (WHO):
Underweight: BMI below 18.5
A BMI in this range may indicate that a person is underweight and could be at risk of malnutrition, weakened immune function, or other health complications related to insufficient body weight.Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
Individuals with a BMI in this range are generally considered to have a healthy weight. This category is associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension.Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
A BMI in this range suggests that a person is carrying excess weight, which may put them at a higher risk for conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and certain cancers.Obese: BMI of 30 or higher
Obesity is linked to serious health risks, including heart disease, stroke, diabetes, sleep apnea, and certain cancers. A BMI in this category indicates the need for health interventions to manage weight and reduce these risks.
How to Use a BMI Calculator
Using a BMI calculator is a simple process, typically requiring just a few steps:
- Enter Your Weight: Depending on the calculator, you can input your weight in either kilograms (kg) or pounds (lbs).
- Enter Your Height: Similarly, input your height in either meters (m) or feet and inches (ft/in).
- Click "Calculate": Once your information is entered, hit the calculate button. The calculator will provide you with your BMI score.
- Review the Result: The result will be displayed along with a corresponding BMI category (underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese). Some calculators may also provide additional health recommendations based on your BMI.
Benefits of Using a BMI Calculator
- Quick and Easy: One of the key benefits of using a BMI calculator is its simplicity. You can quickly enter your details and receive an instant result.
- Easy Accessibility: BMI calculators are widely available on the internet and in mobile apps, making them accessible to nearly everyone.
- Health Screening: BMI is an important screening tool to identify individuals who may be at risk for obesity-related health conditions. It helps individuals monitor their weight over time and take necessary steps if their BMI indicates an unhealthy range.
- Motivation: For those who are actively trying to lose or gain weight, a BMI calculator provides an easy way to track progress and set weight management goals.
Limitations of BMI Calculators
While BMI is a useful tool, it is not without its limitations. It is important to understand that BMI is just one indicator of health and does not capture the full complexity of an individual’s health. Some of the key limitations of BMI include:
- Doesn’t Measure Body Fat Directly: BMI does not differentiate between muscle and fat. A highly muscular person may have a high BMI but have little body fat, potentially skewing the results.
- Doesn’t Consider Fat Distribution: BMI does not indicate where fat is stored in the body. For example, abdominal fat (visceral fat) is more dangerous to health than fat in other areas of the body, but BMI doesn’t distinguish between these types.
- Not Suitable for Children or Seniors: The standard BMI categories are not appropriate for children or elderly individuals, as their body composition and health needs differ from those of adults.
- Cultural and Ethnic Differences: Different populations may experience different health risks at the same BMI levels. For example, people of Asian descent may be at higher risk for health conditions like diabetes at lower BMI thresholds compared to people of European descent.
- Does Not Consider Other Health Factors: BMI does not account for factors such as physical activity, diet, blood pressure, or cholesterol levels—all of which are essential to determining a person’s overall health.
Alternatives and Supplements to BMI
Given the limitations of BMI, other metrics can provide additional insights into health:
- Waist-to-Hip Ratio (WHR): This ratio compares the circumference of your waist to that of your hips. A higher WHR can indicate a greater risk of heart disease and other health problems associated with abdominal fat.
- Body Fat Percentage: Body fat percentage is a more accurate measure of body composition. Unlike BMI, it directly measures the proportion of fat in your body.
- Waist Circumference: Measuring the circumference of your waist can also help identify whether you carry excess fat in your abdominal area, which is a risk factor for several diseases.
Conclusion
BMI calculators are valuable tools for quickly assessing whether a person’s weight falls within a healthy range relative to their height. While BMI is a useful screening tool, it should not be relied upon exclusively for determining health status. Other factors, such as muscle mass, fat distribution, and overall lifestyle habits, must also be considered.
If your BMI falls outside the healthy range, or if you are concerned about your weight or health, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a more comprehensive evaluation. Despite its limitations, BMI remains an accessible and widely used tool for raising awareness about the importance of maintaining a healthy body weight and making informed decisions about health and wellness.