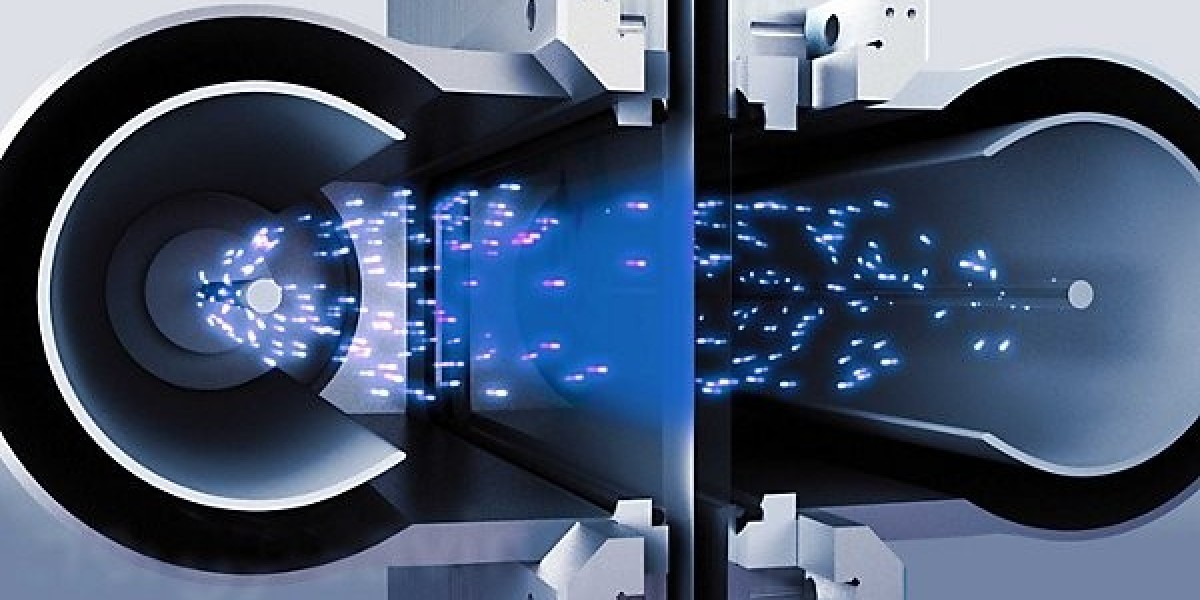
In modern manufacturing, the ability to join dissimilar metals has become a critical requirement for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Traditional welding techniques often fall short in creating strong, reliable joints between metals with differing melting points or thermal properties. Electron Beam (EB) welding has emerged as a groundbreaking solution, offering unmatched precision, strength, and quality for joining dissimilar materials.
This post explores how EB welding excels at joining dissimilar metals, its benefits, and its applications across various industries. For an in-depth understanding of EB welding technology and its capabilities, visit https://ebeammachine.com/electron-beam-welding-the-ultimate-guide-to-high-precision-metal-joining/.
The Challenges of Welding Dissimilar Metals
Joining two different metals presents unique challenges:
- Differing Melting Points: Metals with varying melting points can result in weak joints if heat is not precisely controlled.
- Thermal Expansion: Differences in thermal expansion coefficients can cause warping, cracking, or distortion during welding.
- Metallurgical Incompatibility: Some metals form brittle intermetallic compounds when fused, reducing joint strength.
- Contamination: Traditional welding methods often introduce impurities that weaken the bond.
Why EB Welding Excels at Joining Dissimilar Metals
1. Precise Heat Application
EB welding uses a focused beam of electrons to deliver controlled heat directly to the weld joint. This precision minimizes the risk of overheating one material while ensuring complete fusion.
- Example: Aluminum and titanium, which have vastly different melting points, can be joined seamlessly using EB welding.
2. Minimal Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
The localized energy of the electron beam minimizes the heat-affected zone, preserving the mechanical properties of both metals and reducing stress at the joint.
- Benefit: Improved structural integrity and reduced risk of cracking or distortion.
3. Vacuum Environment
EB welding occurs in a vacuum chamber, eliminating contamination from atmospheric gases. This ensures a clean, defect-free weld, even with dissimilar metals.
- Example: Aerospace manufacturers use EB welding to join titanium and stainless steel for critical components like fuel lines.
4. Strong, Reliable Joints
By precisely controlling the energy input and welding parameters, EB welding creates joints with high strength and durability, even between metals with incompatible properties.
- Benefit: Extended lifespan and improved performance of welded components.
5. Ability to Form Complex Geometries
EB welding allows manufacturers to join dissimilar metals in intricate shapes or configurations, making it ideal for advanced designs.
- Example: Automotive manufacturers use EB welding to join aluminum and high-strength steel in lightweight vehicle frames.
Applications of EB Welding for Dissimilar Metals
1. Aerospace
The aerospace industry demands lightweight, high-strength components that often require joining dissimilar metals. EB welding excels in creating reliable joints for critical applications.
- Use Case: Aluminum-titanium joints in aircraft structures reduce weight while maintaining strength and corrosion resistance.
2. Automotive
Automotive manufacturers rely on EB welding to produce lightweight, fuel-efficient vehicles by combining different metals with optimal properties.
- Use Case: Joining aluminum with magnesium or steel for car frames and battery enclosures enhances performance and efficiency.
3. Medical Devices
In the medical field, EB welding ensures biocompatibility and precision for devices that combine metals like titanium and stainless steel.
- Use Case: Surgical tools and implants require defect-free, strong joints that can withstand sterilization processes.
4. Energy Sector
From renewable energy systems to power plants, EB welding enables the joining of dissimilar metals for high-performance components.
- Use Case: Copper-stainless steel joints in heat exchangers improve thermal conductivity and durability.
5. Defense
In defense applications, EB welding creates robust, reliable components by joining dissimilar metals used in armor, weaponry, and military vehicles.
- Use Case: Titanium-steel joints in armored vehicles enhance durability and weight efficiency.
Advantages of EB Welding for Dissimilar Metals
1. Enhanced Design Flexibility
EB welding enables manufacturers to use the best material for each part of a component, optimizing performance and reducing costs.
2. Reduced Material Waste
By precisely controlling the welding process, EB welding minimizes waste, saving costs and supporting sustainability.
3. Faster Production
The ability to create strong joints in a single pass reduces production time, increasing efficiency.
4. Greater Performance
Components joined with EB welding demonstrate superior performance in terms of strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
Innovations in EB Welding for Dissimilar Metals
AI-Driven Welding
Artificial intelligence is being integrated into EB welding systems to optimize parameters for joining dissimilar metals, ensuring consistent quality.
Advanced Material Science
Ongoing research into welding-compatible alloys is expanding the range of metals that can be joined using EB welding.
Real-Time Monitoring
IoT-enabled sensors track welding conditions and adjust parameters in real time, improving the quality of dissimilar metal joints.
Challenges in Welding Dissimilar Metals and EB Welding Solutions
Metallurgical Compatibility: Some metal combinations naturally form brittle compounds.
- Solution: EB welding’s precision allows for the use of interlayers or controlled cooling to manage compatibility.
Initial Cost of Equipment: EB welding systems require a significant upfront investment.
- Solution: Long-term benefits, including reduced waste, faster production, and superior joint quality, offset the costs.
Skilled Labor Requirements: Operating EB welding systems requires specialized training.
- Solution: Comprehensive training programs and advanced automation tools make the technology more accessible.
Explore More About EB Welding
To learn more about EB welding and its capabilities in joining dissimilar metals, visit https://ebeammachine.com/electron-beam-welding-the-ultimate-guide-to-high-precision-metal-joining/. This guide provides detailed insights into how EB welding is transforming modern manufacturing.
Conclusion
Electron Beam welding has revolutionized the process of joining dissimilar metals, offering unmatched precision, strength, and versatility. From aerospace and automotive to medical devices and energy systems, EB welding meets the demands of industries that require reliable, high-performance joints.
As technology continues to advance, the applications of EB welding for dissimilar metals will expand further, driving innovation and efficiency. Whether you’re manufacturing lightweight vehicle components or high-strength aerospace structures, EB welding provides the solutions you need to succeed