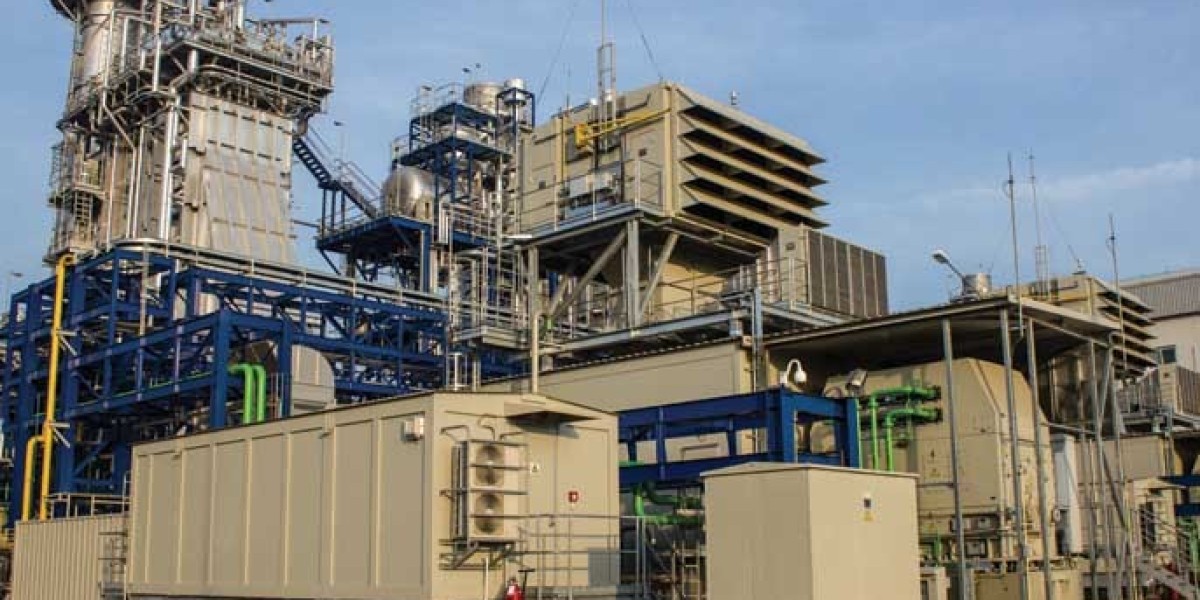
Emergence of Captive Power Plant
With growing energy needs of industries and expensive power supplied by state electricity boards, many large energy intensive companies started setting up their own power generation facilities known as Autoproducers in late 1990s. As these plants generated power primarily for captive use of parent company and surplus power if any was supplied to grid, they came to be known as Autoproducers.
Initial Challenges Captive Power Plant
The initial autoproducers set up coal based thermal power plants as coal was easily available fuel. However, land acquisition, environment clearances, availability of trained manpower were some major initial challenges faced. Some states also did not encourage setting up of captive plants those days owing to lobbying from state electricity boards. It required persistent efforts from pioneer companies to get the model recognized.
Rise in Number of Captive Plants
Once the pioneers like Hindalco, BALCO, NTPC etc. demonstrated technical and financial viability of Captive Power Plant model, many industrial majors eagerly emulated the same. Availability of cheap gas also gave fillip to gas based captive plants later. The number of captive plants grew steadily from just 50 plants with capacity of 2500 MW in early 2000s to over 1000 plants with combined capacity of around 60000 MW now.
Fuel Flexibility Attracts Industries
Captive plants provided flexibility to industries in fuel choice as per availability and price - coal, gas, lignite, biomass etc. could be used. This helped industries optimize energy costs. Industries like steel, aluminum, cement, fertilizers benefited greatly through reliable affordable power and improved competitiveness. Petrochemical complexes also set up large gas based captive plants within plant premises.
Better Plant Load Factor Achieved
and poor load factor, captive plants could achieve much higher plant load factors of 85-90% as they operated to cater demands of connected industry. This enhanced the overall efficiency and economics of power generation.
Renewable Energy Integration Growing
Of late, captive plants are also taking the lead in integrating renewable energy sources like solar, wind within their energy portfolio through hybrid models. This helps industries address both energy security and sustainability aspirations in a cost effective manner. Industries like Aditya Birla Group have set an example through solar and hybrid captive plants.
Role in Grid Management
The surplus power from well-maintained captive plants is supplied to Indian electricity grid. This helps in meeting peak demand and grid stability. During times of low demand from parent industries, captive plants double up as merchant generators fetching better rates. Captive plants have thus evolved as reliable partners in India's energy transformation.
Autoproducers have emerged as a win-win model over last two decades for both industries and Indian power sector. Large industries now self-generate over 30% of total commercial and industrial power needs through captive route. Going forward with progressive policies, the potential of captive route through hybrid renewable models can be further tapped for grid scale benefits.
Get More Insights on Captive Power Plant
Identify the language that you favour-
About Author-
Alice Mutum is a seasoned senior content editor at Coherent Market Insights, leveraging extensive expertise gained from her previous role as a content writer. With seven years in content development, Alice masterfully employs SEO best practices and cutting-edge digital marketing strategies to craft high-ranking, impactful content. As an editor, she meticulously ensures flawless grammar and punctuation, precise data accuracy, and perfect alignment with audience needs in every research report. Alice's dedication to excellence and her strategic approach to content make her an invaluable asset in the world of market insights.
(LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/alice-mutum-3b247b137 )