Introduction
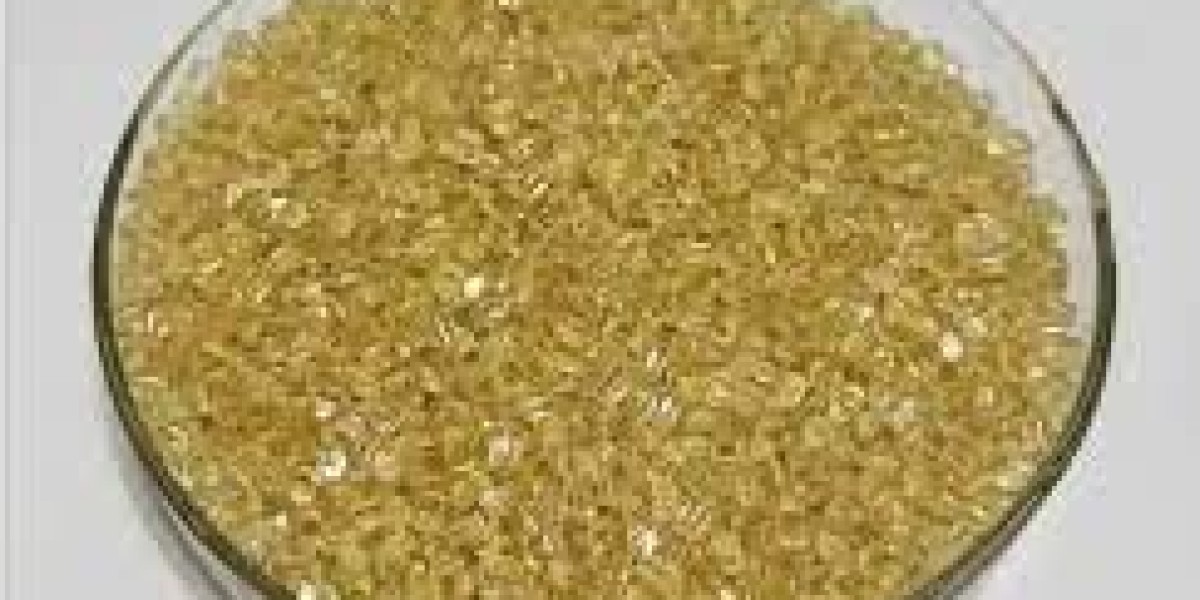
Sulfone polymers are a class of thermoplastic polymers that contain sulfone groups in their chemical structure. The presence of strongly electronegative sulfone groups gives polymers unique properties that make them useful for a variety of engineering applications. Some key properties of polymers include high heat resistance, excellent chemical resistance, good mechanical properties, and higher glass transition temperatures compared to other engineering thermoplastics like polycarbonate or polysulfone. Let's take a deeper look at the chemistry, properties, and applications of polymers.
Chemical Structure and Properties
All polymers are characterized by the presence of sulfone functional groups (S=O2) in their backbone structure. Commonly used polymers include polysulfone (PSU), polyethersulfone (PES), and polyphenylsulfone (PPSU). PSU has an aromatic backbone containing alternating phenylene and sulfone groups. PES is similar but also contains oxyethylene moieties for enhanced flexibility and hydrolytic stability compared to PSU. PPSU replaces the phenylene group with biphenyl, giving it higher glass transition and melting temperatures than PSU or PES.
The sulfone functional group makes these polymers highly heat resistant due to the stability of the carbon-sulfur double bond. Polymers typically have continuous use temperatures of 170-230°C depending on the specific polymer and processing history. They also exhibit excellent chemical resistance, being insoluble in most alkalis, acids, chloride solutions, and organic solvents except polar aprotic solvents like dimethylformamide (DMF) and dimethylacetamide (DMAc). This chemical resilience extends product lifetimes. Mechanical properties are also very good, with high stiffness, strength, and dimensional stability. Glass transition temperatures range from 185-240°C, significantly higher than other engineering thermoplastics.
Film and Sheet Applications
Due to their processability, strength, clarity, and chemical resistance, these polymers see widespread use as films and sheets for various applications. PSU and PES film finds use as insulation for wire and cables up to 600 volts. Their heat resistance allows operation in harsh outdoor environments or high-temperature industrial settings. Sulfone films also find use as insulation for transformers, capacitors, and other electronic components requiring thermal and chemical insulation.
In the medical field, transparent PSU and PPSU films and sheets are used for dialysis applications like hemodialyzers and blood oxygenators due to their non-thrombogenic properties and ability to withstand frequent steam sterilization cycles. These polymer films are also becoming more common as transparent glazing materials in medical and laboratory equipment.
Membranes and Filtration Materials
Another major application area is in the production of filtration membranes from these polymers. Due to their hydrolytic stability, PES membranes are widely used for microfiltration and ultrafiltration in applications like water purification, food and beverage processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing. They can withstand acidic or basic cleaning chemicals required to sterilize membrane modules.
Within the medical field, the polymer membranes are commonly used for hemodialysis, hemofiltration, plasma separation, and blood oxygenation applications. PES and PPSU membranes offer high flow rates and sieving characteristics needed for efficient dialysis while remaining non-thrombogenic. Their chemical stability allows extended use compared to cellulose-based membranes. Sulfone membranes are also increasing being used for applications like reverse osmosis and nanofiltration due to their high strength and fouling resistance.
Molded Components and Engineering Plastics
The mechanical properties and heat resistance of these polymers make them viable engineering plastics for injection molding or extrusion of durable components. For automotive and industrial uses, PSU and PES are injection molded into parts like distributor casings, electric motor housings, electrical switches, and connectors. Their high heat deflection allows these components to withstand prolonged high-temperature operation.
Electronics is another major sector utilizing injection molded PSU, PES, and PPSU components. Common applications include housings for mobile devices, connectors, switches, small appliances, and wire insulation. These polymer components offer heat resistance, impact strength, and electrical insulation at temperatures far exceeding other engineering plastics. Within healthcare, PSU and PPSU are injection molded into durable tubing, cassette housings, connectors and fluid management devices.
Fibers and Filaments
While less common than other major applications, these polymers can also be melt spun into high-performance fibers and monofilaments. PSU and PES fibers exhibit good strength, abrasion resistance, and retention of properties over a wide temperature range. They see niche use as insulating wraps, monofilaments for sewing and suturing medical devices. Hydrolytic stability also makes PES attractive for use in filtration membranes in the form of woven or nonwoven fibers.
Experimental research has also looked at spinning PES into hollow fibers for areas like tissue engineering scaffolds and forward osmosis membranes. The combination of strength, biocompatibility and hydrolytic stability could make sulfone fibers promising materials for advanced filtration and biomedical applications if production costs can be lowered.
Advantages, Limitations and Alternatives
To summarize, these polymers offer advantageous properties for their applications including heat resistance up to 230°C, strong chemical resistance to acids/bases/solvents, good mechanical properties and high Tgs. However, they also have some limitations. These polymers can be more expensive than other engineering thermoplastics like polyetherimide or polycarbonate. They also have a hydrophilic character that can lead to moisture absorption if not properly sealed.
In terms of alternatives, for generalized engineering uses where cost is important, polyetherimide (PEI) or polyphenylene oxide (PPO) thermoplastics may be suitable options. polycarbonate (PC) could compete on cost but has lower heat resistance. For filtration applications needing hydrolytic stability, cellulose-based or polysulfide materials are main alternatives to sulfone polymer membranes and fibers. Overall though, the unique balance of properties offered by sulfone polymers still make them preferred choices for many high-performance applications.
Search
- Friendly Websites www.wsisw.com www.bybit.com www.temu.com www.ebay.com www.adsy.com www.iherb.com www.whmcs.com www.secsers.com www.cambly.com www.binance.com www.displate.com www.magenet.com www.gainrock.com www.seoclerks.com www.aliexpress.com www.freelancer.com www.rankranger.com www.wehaveoffer.com www.qrmenutable.com www.coinpayments.net www.linksmanagement.com
Popular Posts