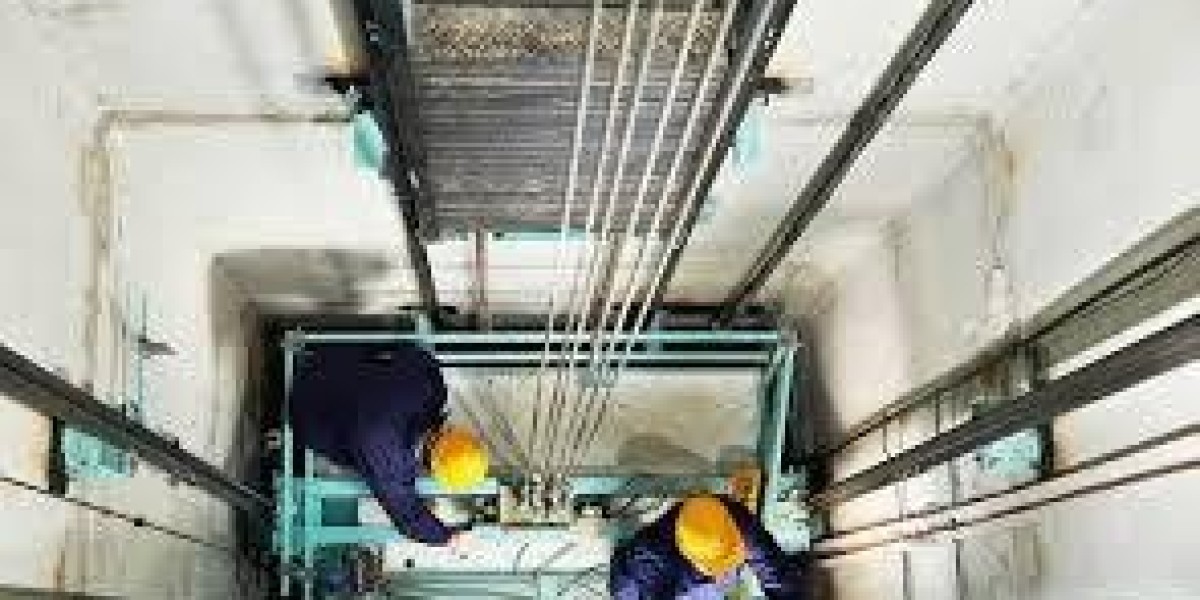
Dumbwaiters, often seen as a convenience in homes and commercial spaces, are small freight elevators designed to transport goods between different floors. While they offer numerous practical benefits, their environmental impact deserves consideration, especially as we strive for sustainability in our daily operations. Below, we explore the environmental implications of using dumbwaiters.
1. Energy Efficiency
Reduced Energy Consumption: Dumbwaiters typically consume less energy compared to traditional elevators. They often require less power to operate due to their smaller size and lighter loads, making them a more energy-efficient choice, particularly in low-rise buildings.
Potential for Energy Recovery: Some modern dumbwaiters are designed with energy recovery systems that harness energy during operation. This can further reduce overall energy consumption and lower carbon footprints.
2. Sustainable Materials and Construction
Eco-Friendly Materials: When selecting a dumbwaiter, opting for models constructed with sustainable materials can minimize environmental impact. Many manufacturers are now using recycled and eco-friendly materials in their designs.
Durability and Lifespan: A well-constructed dumbwaiter can have a long lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. Choosing high-quality products ensures durability and longevity.
3. Space and Resource Optimization
Maximized Space Efficiency: Dumbwaiters help optimize space in residential and commercial settings, allowing for more efficient use of vertical space. This can lead to reduced overall building sizes and less land use, indirectly contributing to lower environmental footprints.
Improved Logistics: In commercial environments, dumbwaiters streamline logistics by allowing quick and efficient movement of goods. This can decrease the need for multiple trips by staff, thereby reducing energy consumption associated with transport.
4. Reduction in Human Labor
Lower Labor Emissions: By automating the movement of goods, dumbwaiters can reduce the reliance on human labor for transporting items between floors. This can lead to lower emissions from vehicles used in transporting goods across larger spaces.
Enhanced Efficiency: Automating the transportation of goods can also lead to increased efficiency in operations, thereby minimizing resource consumption and reducing waste in the supply chain.
5. Waste Reduction
Minimizing Physical Strain: Dumbwaiters can help prevent physical strain on workers, reducing potential injuries and the associated costs of medical care and lost productivity. This promotes a healthier work environment and contributes to less waste in healthcare resources.
Improved Waste Management: In settings like restaurants or hotels, dumbwaiters can facilitate more efficient waste disposal. By transporting waste directly to disposal areas, they can minimize clutter and optimize waste management processes.
6. Environmental Considerations in Manufacturing
Responsible Manufacturing Practices: It is essential to choose manufacturers that prioritize sustainability in their production processes. This includes using energy-efficient machinery, minimizing waste during manufacturing, and adhering to environmental regulations.
End-of-Life Recycling: Many modern dumbwaiters are designed with recyclability in mind. Choosing systems that can be easily disassembled and recycled at the end of their lifespan reduces landfill waste and promotes a circular economy.
7. Potential Drawbacks
Electrical Waste: While dumbwaiters are generally more energy-efficient, they still require electricity for operation. In areas where electricity is generated from fossil fuels, this can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Installation Impact: The installation of dumbwaiters may require alterations to existing structures, potentially generating waste materials during construction. Choosing installation practices that minimize disruption and waste is crucial.
Conclusion
While dumbwaiters provide practical benefits in terms of convenience and efficiency, their environmental impact is multifaceted. By understanding and addressing factors such as energy efficiency, sustainable materials, and responsible manufacturing practices, users can make informed choices that align with their environmental goals.
Ultimately, the responsible use of dumbwaiters can contribute to a more sustainable future, promoting efficiency and reducing resource consumption in various settings. As we continue to explore environmentally friendly solutions, dumbwaiters can be an integral part of the conversation surrounding sustainability in architecture and design.