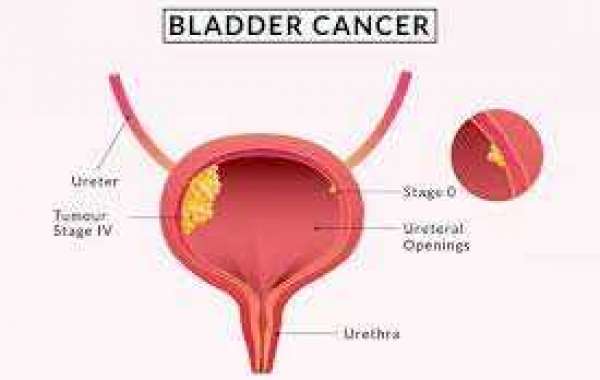
Bladder cancer is a condition that arises when abnormal cells in the bladder multiply uncontrollably. The bladder, a hollow organ in the lower abdomen, stores urine produced by the kidneys. While bladder cancer is more common in older adults, it can affect individuals of any age. This article delves into the intricacies of bladder cancer, exploring its characteristics and the complexities associated with cancer recurrence.
Bladder Cancer Overview:
What is bladder cancer? Bladder cancer typically begins in the urothelial cells lining the bladder's inner surface. This form is known as urothelial carcinoma, comprising the majority of bladder cancer cases. Less common types include squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma.
Risk Factors:
Understanding risk factors is crucial in grasping bladder cancer's dynamics. Smoking stands out as a primary risk factor, with smokers being at a higher risk compared to non-smokers. Other risk factors include exposure to certain chemicals, chronic bladder inflammation, family history of bladder cancer, and being older than 40.
Symptoms:
Bladder cancer symptoms can manifest subtly, making early detection challenging. Common signs include blood in urine, frequent urination, pain during urination, and pelvic pain. Recognizing these symptoms prompts timely medical evaluation, enhancing the chances of early detection and effective treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis often involves a combination of imaging tests, cystoscopy, and biopsy to determine the cancer type and stage. Treatment approaches vary based on factors such as the cancer stage, type, and the patient's overall health.
Surgery: Surgical interventions may involve removing tumors, part of the bladder (partial cystectomy), or the entire bladder (radical cystectomy). In some cases, a urinary diversion is necessary to reroute urine.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy, administered intravenously or directly into the bladder, targets cancer cells throughout the body or locally. It can be used before or after surgery to enhance treatment outcomes.
Immunotherapy: Some cases benefit from immunotherapy, which stimulates the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy, a form of immunotherapy, is commonly used for early-stage bladder cancer.
Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays target cancer cells, often used in combination with surgery or as a primary treatment for specific cases.
Bladder Cancer Recurrence:
While treatment aims to eradicate cancer, the risk of recurrence remains a significant concern. Bladder cancer recurrence can happen in the bladder or other areas, presenting challenges for both patients and healthcare providers.
Factors Influencing Recurrence:
Several factors contribute to the likelihood of bladder cancer recurrence. High-grade tumors, tumors invading the muscle layer of the bladder, and a history of recurrence are indicators of increased risk. Smoking cessation and adherence to post-treatment surveillance play pivotal roles in minimizing recurrence chances.
Monitoring and Surveillance:
After initial treatment, regular follow-up appointments and surveillance are essential. Cystoscopy, imaging tests, and urine cytology may be part of routine monitoring. Surveillance frequency depends on the cancer stage and the risk of recurrence.
Coping with Recurrence:
Coping with bladder cancer recurrence involves a multidimensional approach. Emotional support, open communication with healthcare providers, and lifestyle modifications contribute to navigating the challenges.
Emotional Support: Dealing with cancer recurrence can evoke a range of emotions. Seeking support from friends, family, or a support group helps in processing these emotions and gaining perspective.
Communication with Healthcare Providers: Transparent communication with healthcare providers is crucial. Understanding the reasons behind recurrence, potential treatment options, and proactive measures enhances the patient's ability to make informed decisions.
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress management, contributes to overall well-being. Smoking cessation, if applicable, is particularly vital in reducing the risk of recurrence.
Conclusion:
Bladder cancer, with its multifaceted nature, demands a comprehensive understanding for effective management. Early detection, personalized treatment, and vigilant post-treatment surveillance are pivotal in addressing both the primary disease and the challenges associated with recurrence. Navigating the complexities of bladder cancer requires a collaborative effort involving healthcare providers, patients, and support networks, fostering a proactive approach towards treatment, monitoring, and overall well-being.