The global drone sensors market size is projected to reach USD 2,342.1 million by 2028, exhibiting a CAGR of 25.08% during the forecast period. The increasing deployment of drones amid the COVID-19 crisis will be a major driving factor for this market, postulates Fortune Business Insights™ in its report, titled ”Drone Sensors Market, 2020-2028”. Drone sensors are critical components that enable unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, to collect and process data for various applications. These sensors play a crucial role in helping drones navigate, gather information, and perform specific tasks.
Informational Source:
https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/drone-sensor-market-102596
Key Companies Covered in Drone Sensors Market are:
- Trimble (US)
- Bosch Sensortec (Germany)
- TDK InvenSense (U.S.)
- Sparton NavEx (US)
- Raytheon (US)
- AMS AG (Austria)
- Flir System (U.S.)
- KVH Industries (U.S.)
- TE connectivity (Switzerland)
- Lord MicroStrain (U.S.)
- Other Players
Here's an overview of some of the key types of sensors used in drones:
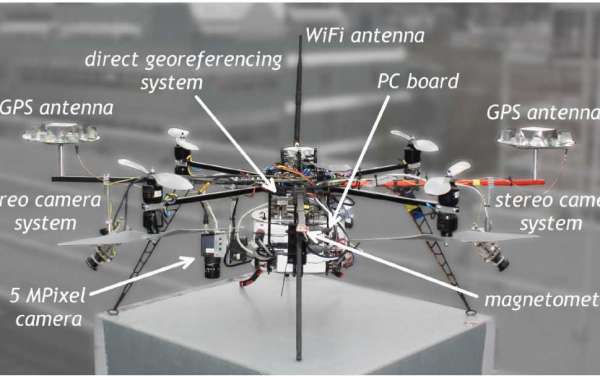
GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS receivers are fundamental sensors in drones, providing accurate location and altitude information. They enable drones to determine their position in real-time, follow predefined flight paths, and assist in various applications like aerial photography and mapping.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU): IMUs consist of accelerometers and gyroscopes, which measure changes in velocity and orientation. IMUs help drones maintain stable flight and provide data for attitude control and stabilization.
Barometric Altimeter: Barometric altimeters measure atmospheric pressure, allowing drones to determine their altitude above sea level. This data is essential for maintaining the drone's flight stability and for avoiding collisions with the ground or obstacles.
Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging): Lidar sensors emit laser pulses and measure the time it takes for the light to bounce back. This technology provides high-precision 3D mapping and obstacle detection capabilities, making it invaluable for applications such as terrain modeling, forestry management, and obstacle avoidance.
Ultrasonic and Infrared Sensors: These sensors use sound waves or infrared light to measure distances to nearby objects. They are often used for low-altitude obstacle avoidance and landing assistance.
RGB and Multispectral Cameras: Drones are commonly equipped with RGB (Red, Green, Blue) cameras for capturing high-resolution images and videos. Multispectral cameras, on the other hand, capture data beyond the visible spectrum, such as infrared and ultraviolet, to aid in agriculture, environmental monitoring, and other applications.
Thermal Cameras: Thermal sensors, also known as thermal cameras or infrared cameras, detect temperature differences in the environment. They are essential for applications like search and rescue, building inspection, and wildlife monitoring.
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) Receivers: In addition to GPS, drones may use other GNSS systems like GLONASS or Galileo for more precise and reliable positioning in areas with obstructed or weak GPS signals.
Magnetometer: Magnetometers measure the Earth's magnetic field, helping drones determine their heading and orientation. They are crucial for accurate compass readings and navigation in various conditions.
Air Quality and Gas Sensors: Some drones are equipped with sensors to measure air quality parameters, including carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter. These sensors find applications in environmental monitoring and industrial inspections.
Hydrological and Environmental Sensors: For water-related applications, drones can be equipped with sensors for measuring parameters like water quality, temperature, and turbidity. These sensors are valuable for aquatic research and monitoring.
Radar Systems: Radar sensors, like Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), are used for all-weather and day/night imaging. They are commonly employed in applications such as agriculture, forestry, and disaster response.
Sonar Sensors: In underwater drones (also known as autonomous underwater vehicles or AUVs), sonar sensors are used for navigation, mapping, and obstacle avoidance in aquatic environments.
The choice of sensors depends on the specific application of the drone, as different sensors provide data for different purposes. Advances in sensor technology and miniaturization have expanded the capabilities of drones, making them increasingly versatile tools for a wide range of industries, including agriculture, construction, surveying, environmental monitoring, and public safety.