Ultrasonic welding is an efficient and environmentally friendly bonding technology widely used in lithium battery manufacturing. It achieves molecular bonding between materials through high-frequency vibration energy, ensuring the durability and conductivity of welded components. This article delves into the applications and advantages of ultrasonic welding technology in lithium battery components.
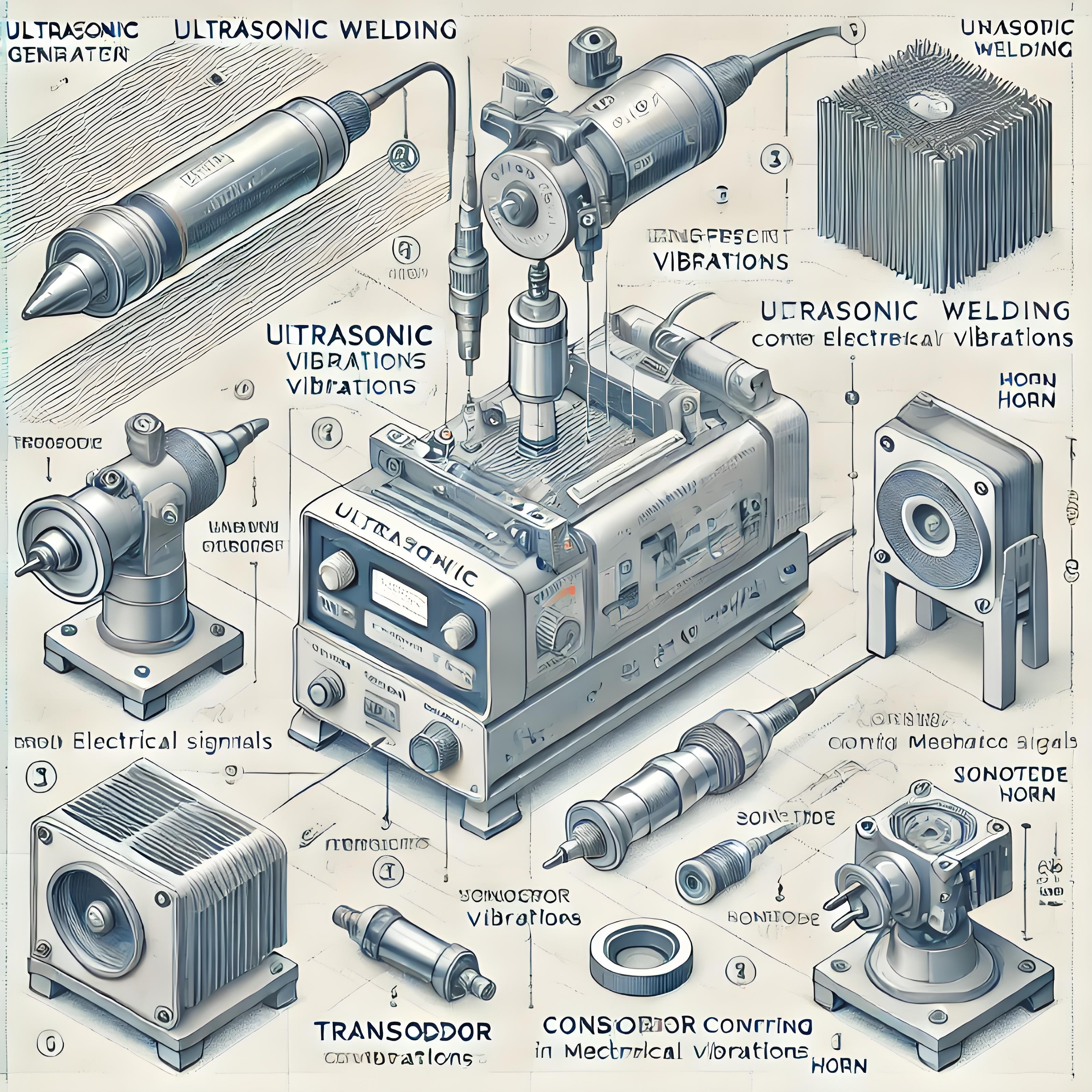
1. Principles and Characteristics of Ultrasonic Welding Technology
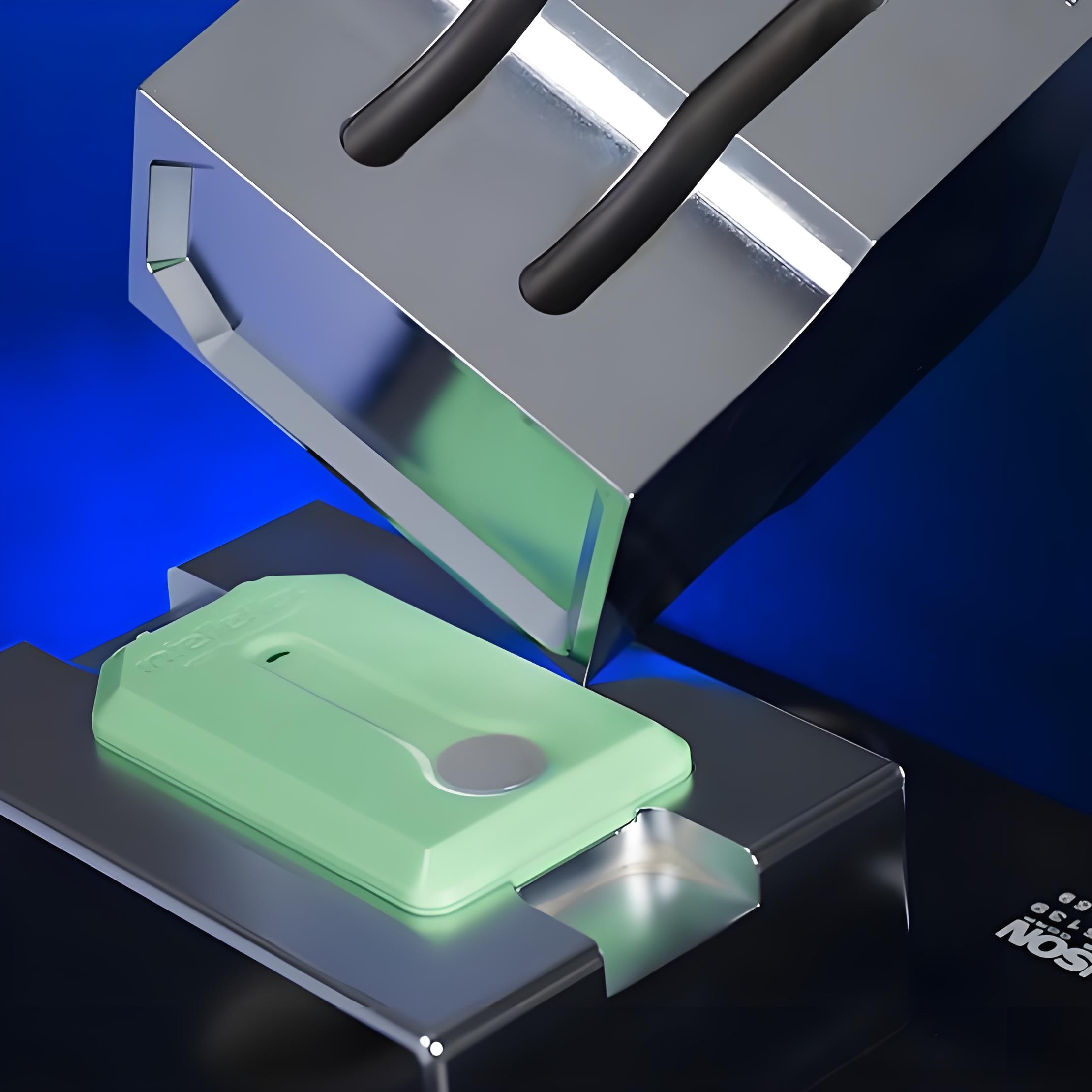
Ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency mechanical vibrations to generate frictional heat at the contact surface, causing the materials to interweave and fuse. No adhesives or solder are required; welding is achieved solely through vibration and pressure.
Key Characteristics
High Efficiency: Welding is completed in just a few seconds.
Eco-Friendly: No smoke or waste is produced, meeting environmental standards.
Wide Applicability: Suitable for various materials, including copper, aluminum, and nickel.
High Precision: Enables precise welding of complex components.
2. Applications of Ultrasonic Welding in Lithium Battery Components
Lithium batteries are complex structures comprising cathodes, anodes, separators, electrolytes, and casings. Ultrasonic welding plays a critical role in the following components:
1. Tab Welding
The cathode and anode tabs are welded to conductive plates or busbars, ensuring efficient current transfer.
2. Cell Connection
In multilayer cell stacks, ultrasonic welding enhances electrical conductivity and mechanical strength between cells.
3. Module Assembly
In battery modules, multiple cells are welded into a single unit to support high current output and stable performance.
4. Protection Circuit Welding
The protection circuit module (PCM) is welded to the cells, ensuring the safe operation of the battery pack.
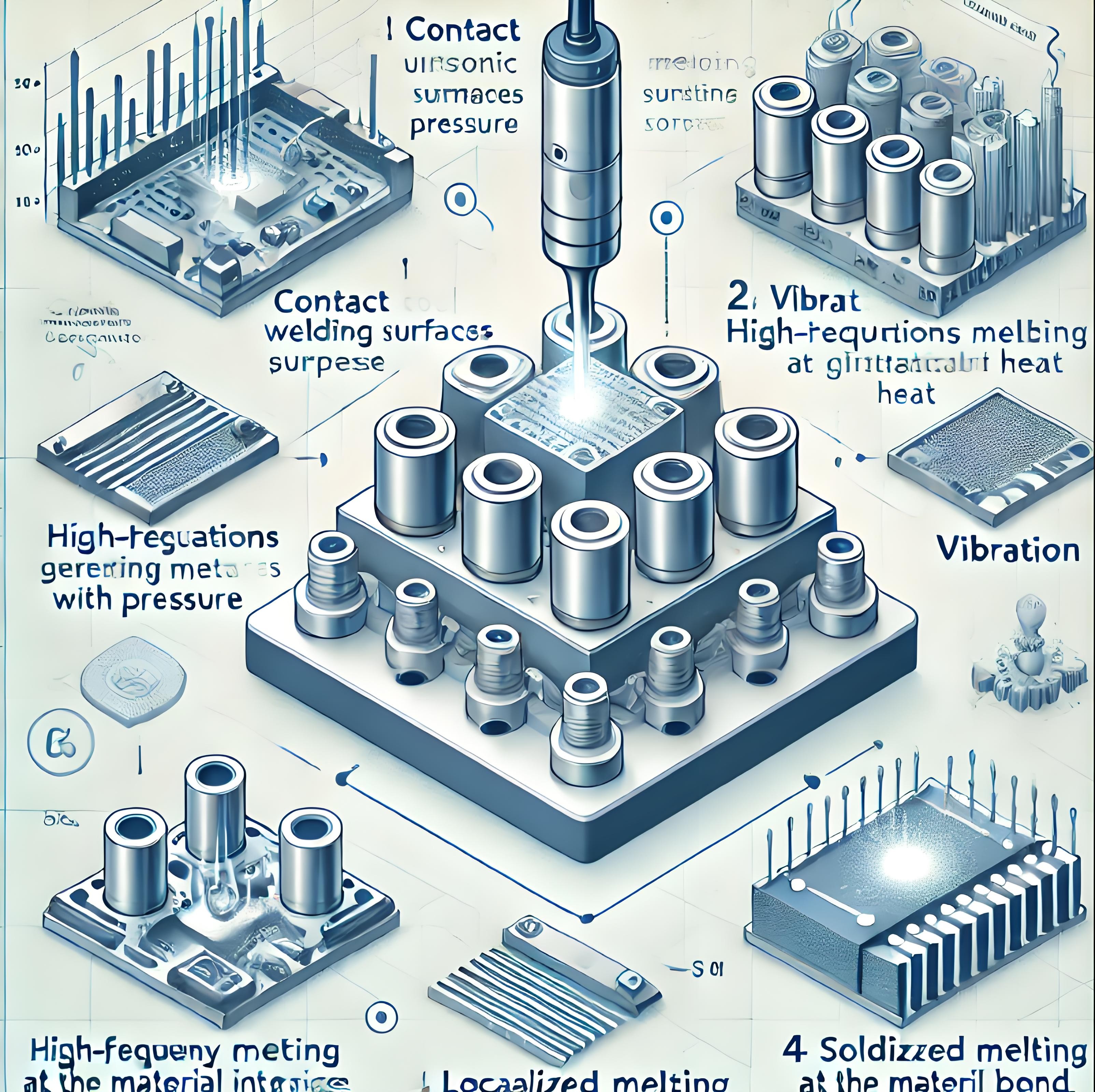
3. Ultrasonic Welding Process
Process Flowchart
StepDescription1. Surface CleaningRemove oxides and impurities from the surfaces to ensure weld quality.2. Clamping and PositioningSecure the components in the welding equipment to ensure precise positioning during welding.3. Ultrasonic VibrationThe welding horn transmits high-frequency vibration energy, causing the contact surfaces to heat and melt through friction.4. Material BondingAfter melting, the surfaces cool and form a strong weld joint.5. Quality InspectionTest the weld points for conductivity and mechanical strength to ensure compliance with standards.
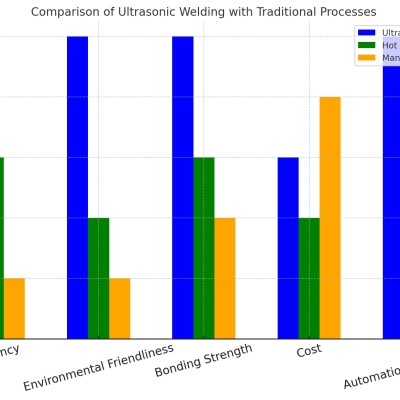
4. Comparison Between Ultrasonic Welding and Traditional Welding
Technology Comparison Table
FeatureUltrasonic WeldingTraditional WeldingWelding SpeedFast, completed in secondsSlower, takes several minutesOperating TemperatureNo high temperature requiredRequires high temperatureEco-FriendlinessNo smoke or wasteMay produce smoke and slagMaterial CompatibilitySuitable for both metals and non-metalsPrimarily suitable for metalsAutomation LevelHigh, supports large-scale automationLow, requires more manual intervention
5. Advantages and Precautions of Ultrasonic Welding
1. Advantages
High Reliability: Weld points exhibit excellent conductivity and mechanical strength.
Low Energy Consumption: Consumes less energy compared to traditional welding.
High Flexibility: Suitable for components of various shapes and sizes.
2. Precautions
Material Selection: Ensure that the materials have good acoustic properties.
Parameter Settings: Adjust power, pressure, and amplitude based on material and welding requirements.
Welding Horn Maintenance: Regularly inspect the horn to prevent wear from affecting weld quality.
6. Future Trends
With the rapid growth of the electric vehicle and energy storage markets, the demand for lithium batteries is soaring, driving the continuous advancement of ultrasonic welding technology. Key future trends include:
Higher Automation Levels: Enhancing efficiency and consistency through intelligent equipment.
Compatibility with New Materials: Developing welding techniques for novel battery materials.
Process Optimization: Further refining welding parameters to improve quality.https://mechtechsupply.com/pro....duct-category/ultras