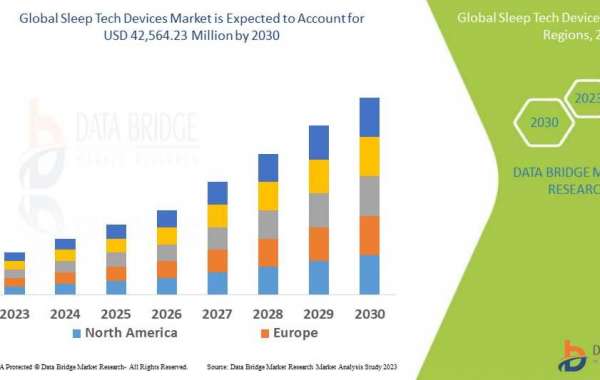
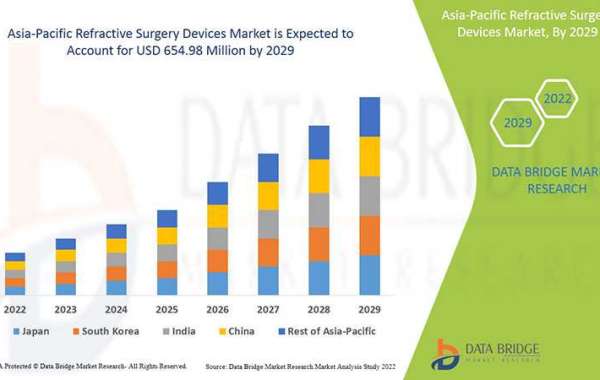
Composition of Lok Sabha
The composition of the Lok Sabha, the lower house of the Indian Parliament, is determined by the number of seats allocated to each state and union territory. The total number of seats is currently 543, with 530 allocated to the states and 13 to union territories. These seats are distributed among the states and union territories in a manner such that the population of each constituency is roughly the same. The Lok Sabha is elected every five years through a general election, in which citizens of India over the age of 18 are eligible to vote. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected through a first-past-the-post system, in which the candidate with the most votes in each constituency is elected.
1947 partition of India and Pakistan
The 1947 partition of India and Pakistan refers to the division of British India into two independent countries, India and Pakistan, on August 15th, 1947. This event marked the end of British colonial rule in India and the beginning of a new era in South Asian history. The partition was based on religious divisions, with Pakistan becoming a Muslim-majority country and India remaining predominantly Hindu. The partition led to one of the largest mass migrations in history, with millions of people moving across the newly-drawn border in search of safety and a new home. The process was accompanied by widespread violence and loss of life, with estimates of the number of deaths ranging from several hundred thousand to over a million. The partition remains a contentious issue to this day, with ongoing disputes between India and Pakistan over issues such as the status of Kashmir.