In modern infrastructure development, the need for durable, efficient, and cost-effective materials is more crucial than ever. One such material that has gained significant recognition is the Uniaxial Geogrid for Road Construction. Used for soil reinforcement, stabilization, and load distribution, uniaxial geogrids have become a key component in both road building and retaining wall projects. This article explores the importance of uniaxial geogrids, their installation process, and how they are applied in retaining wall systems.
What is Uniaxial Geogrid?
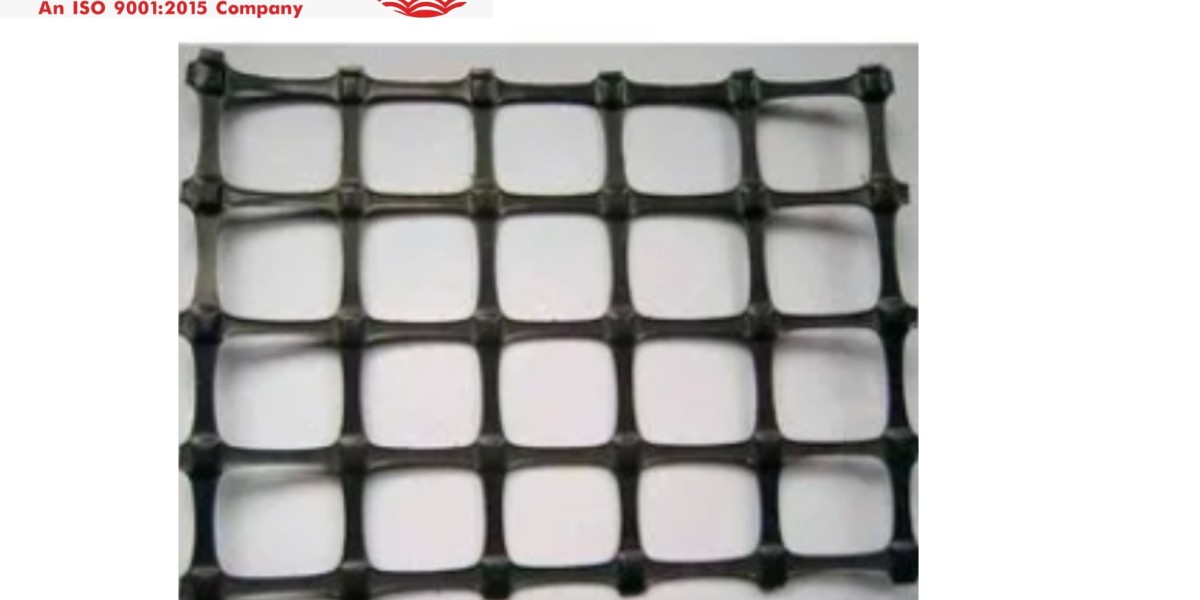
A Uniaxial Geogrid is a high-strength, polymeric grid structure used primarily for the reinforcement of soils. Unlike biaxial geogrids, which distribute loads in both horizontal and vertical directions, uniaxial geogrids are designed to distribute loads in one direction—either horizontally or vertically. This makes them particularly suitable for applications where soil needs to be reinforced in a specific direction, such as in retaining walls or embankments.
The material is usually made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene, offering excellent durability and resistance to harsh environmental conditions. The open grid structure allows soil to interact with the material, which strengthens the overall system and improves the load-bearing capacity of the soil.
The Role of Uniaxial Geogrid in Road Construction
One of the most significant applications of Uniaxial Geogrid for Road Construction is in the reinforcement of weak or unstable soils. When constructing roads over soft or uneven ground, engineers face the challenge of preventing soil movement and ensuring the long-term stability of the roadway. Without proper reinforcement, roads can suffer from cracks, potholes, and uneven surfaces, leading to costly repairs and maintenance.
By using uniaxial geogrids, the load from the road surface is distributed more evenly across the underlying soil. This prevents excessive deformation and helps to maintain the integrity of the road for a longer period. The geogrid works by confining the soil and preventing lateral movement, which in turn enhances the bearing capacity and reduces the risk of settlement.
Moreover, using uniaxial geogrids in road construction reduces the need for deep excavation and expensive base materials. This not only lowers the overall construction costs but also speeds up the construction process, making it an ideal choice for large-scale infrastructure projects.
Uniaxial Geogrid Installation: Best Practices
The process of Uniaxial Geogrid Installation is relatively straightforward but requires careful attention to detail to ensure its effectiveness. The first step in the installation process is site preparation. The area where the geogrid will be installed needs to be cleared of debris, large rocks, and vegetation to create a smooth surface.
Once the area is prepared, the uniaxial geogrid is unrolled over the designated section of soil. The orientation of the geogrid is crucial—since uniaxial geogrids provide reinforcement in only one direction, it must be aligned in the direction of the highest anticipated stress. For instance, in road construction, the geogrid should be placed parallel to the road to reinforce the load-bearing axis.
The geogrid is then secured in place using anchors or pins, ensuring that it remains taut and free from wrinkles. After the grid is secured, soil or aggregate is layered on top of the geogrid and compacted to ensure proper integration between the soil and the grid. This process may be repeated multiple times, depending on the height of the embankment or the number of soil layers required.
Proper Uniaxial Geogrid Installation ensures that the geogrid effectively distributes loads, minimizes soil movement, and enhances the overall stability of the structure. Poor installation can result in ineffective reinforcement, leading to premature failure or increased maintenance costs.
Geogrid Retaining Wall: Strengthening Vertical Structures
Retaining walls are essential for preventing soil erosion and landslides, particularly in areas with steep slopes or unstable ground. These walls are often used in highway construction, landscaping, and residential projects to create level areas on sloped terrain. Geogrid retaining walls are reinforced with geogrid layers to improve their load-bearing capacity and prevent soil movement.
In a Geogrid retaining wall system, layers of uniaxial geogrid are placed between layers of backfill soil. The geogrid extends horizontally from the retaining wall into the soil, creating a reinforced soil structure. This helps distribute the weight of the wall and the retained soil over a wider area, reducing the pressure on the wall and improving its stability.
The use of uniaxial geogrids in retaining walls also allows for the construction of taller walls with steeper angles, as the geogrid provides additional support to resist the forces of gravity and lateral soil pressure. This makes geogrid retaining walls an ideal solution for projects that require significant elevation changes, such as hillside developments or highway embankments.
Additionally, geogrid-reinforced retaining walls are often more cost-effective than traditional concrete walls. By using geogrid and soil reinforcement, engineers can reduce the amount of concrete needed, lowering both material costs and construction time.
Advantages of Using Uniaxial Geogrid in Road and Retaining Wall Construction
Improved Load Distribution: Uniaxial geogrids help to evenly distribute loads across the soil, reducing the risk of deformation and failure in roads and retaining walls.
Cost-Effective: The use of geogrids can reduce the need for expensive base materials and deep excavation, making it a cost-effective option for large infrastructure projects.
Enhanced Durability: Uniaxial geogrids are made from durable materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions, ensuring long-term performance in both road construction and retaining wall applications.
Versatile Applications: Whether used in road construction or retaining walls, uniaxial geogrids are versatile and can be adapted to various soil conditions and project requirements.
Faster Installation: Compared to traditional reinforcement methods, installing uniaxial geogrids is quicker and more efficient, leading to faster project completion times.
Conclusion
The use of Uniaxial Geogrid for Road Construction and geogrid retaining wall systems is a game-changer in modern infrastructure projects. These geogrids provide essential reinforcement, distributing loads and preventing soil movement, which helps to extend the lifespan of roads and retaining walls. Proper Uniaxial Geogrid Installation is key to ensuring that the geogrid performs effectively, providing long-term stability and reducing maintenance costs.
As infrastructure demands continue to grow, geogrids offer a cost-effective, durable, and environmentally friendly solution to the challenges of soil reinforcement and erosion control. Whether for roads or retaining walls, uniaxial geogrids are a reliable choice for engineers and construction professionals looking to improve the resilience of their projects.
Here are Related For Uniaxial Geogrid Installation
Q1: What is the main purpose of Uniaxial Geogrid in road construction?
Ans: The main purpose of Uniaxial Geogrid in road construction is to reinforce the soil, distribute loads evenly, and prevent lateral movement, ensuring the long-term stability and durability of roads.
Q2: How is Uniaxial Geogrid installation carried out?
Ans: Uniaxial Geogrid installation involves preparing the site, unrolling the geogrid over the soil, securing it with anchors, and layering and compacting soil or aggregate over the grid to ensure proper integration and load distribution.
Q3: How does a geogrid retaining wall improve soil stability?
Ans: A geogrid retaining wall improves soil stability by reinforcing the soil layers with uniaxial geogrid, which distributes the weight of the wall and the retained soil, preventing soil movement and reducing lateral pressure on the wall.